Best Tools to Extract Data from Graph Images Without Guesswork
Graph images are often rich in visual data, but without the right tools, pulling out the actual numbers can feel nearly impossible. Whether it’s a bar chart from a PDF, a plot from a research paper, or a snapshot of a dashboard, manually estimating values is neither accurate nor practical. Thankfully, there are tools designed to handle this exact problem—and do it well. Here’s a list of some of the best options available if you’re looking to extract clean, usable data from graph images.
Best Tools to Extract Data from Graph Images
WebPlotDigitizer
WebPlotDigitizer is a browser-based tool built to capture data points from graphs and charts with various shapes—scatter plots, bar charts, maps, and even polar plots. It allows you to define the axis, identify the graph type, and then either click to mark data points or let the software detect them automatically. It supports CSV export and offers batch processing if you have multiple images.
PlotDigitizer
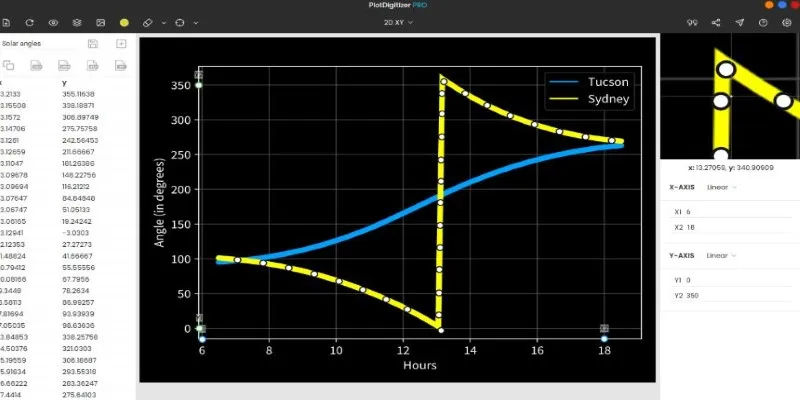
PlotDigitizer is a downloadable software with a clean interface and useful features such as curve tracing, zooming, and layer customization. You can use it to manually digitize data points or enable the auto-detection feature. It handles line, bar, and scatter graphs well and supports formats like PNG, JPEG, and BMP.
Graph Reader
Graph Reader is a desktop application that focuses on simplicity. It works well for basic line and scatter plots. You load the image, define the axes, and click along the curve to create data points. While it doesn’t offer much automation, it works when you need manual precision.
DataThief III
DataThief III has been around for a while and continues to be reliable. It’s Java-based, which means it works across platforms. The tool can automatically trace curves and even interpolate missing data. It also allows calibration using both linear and logarithmic scales, which makes it versatile across various scientific domains.
Engauge Digitizer
Engauge Digitizer is a robust open-source tool with one standout feature: it can process graphs with complex layouts. It offers grid-line removal, color separation, and axis mapping. The software supports both manual and auto- tracing and works well when dealing with cluttered or scanned graphs.
DigitizeIt
DigitizeIt is a commercial tool with a polished interface and professional- level accuracy. It’s known for handling noisy images and has adjustable smoothing settings for better curve recognition. DigitizeIt supports 2D and polar plots, and the export options, including Excel and CSV, are flexible.
OriginPro
OriginPro isn’t just a data extraction tool—it’s a full data analysis suite. However, graph digitization offers built-in tools for tracing data from imported image files. The auto-trace feature is highly accurate, especially when working with high-resolution plots, and the integration with statistical tools is a plus for researchers.
GetData Graph Digitizer
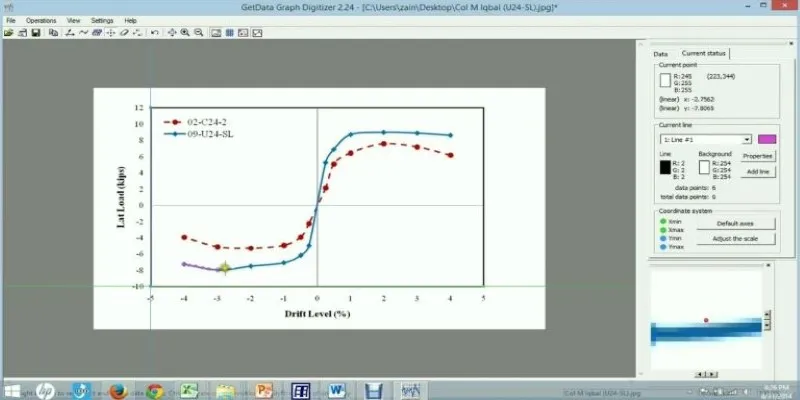
GetData Graph Digitizer is a lightweight and easy-to-use tool for converting image-based graphs into data. It handles different chart types, from line plots to scatter plots and bar charts. You define the axes, calibrate the scale, and click along the lines to extract data. It’s not heavy on automation, but it gives control to the user.
GraphClick
GraphClick is a macOS-exclusive tool that lets you extract data points from any image of a graph or chart. You just load the image, calibrate the axes, and then click along the graph to record data points. It’s especially handy for academic work where you need quick estimates from published figures. The tool supports both linear and logarithmic scales and can export results to text or spreadsheet formats.
PlotReader
PlotReader is an Android app designed to extract data from graph images directly on your phone. It’s helpful when you don’t have access to a desktop or need something lightweight. You take a picture of the graph, mark the axes, and then tap on the data points. It supports multiple graph types and has basic export options. It’s ideal for quick fieldwork or study sessions where you need immediate data access.
How to Use WebPlotDigitizer to Extract Data from Graph Images
All the tools listed above are good in their own way, but if there’s one that stands out for accessibility, accuracy, and a well-thought-out workflow, it’s WebPlotDigitizer. It doesn’t require a download, works directly in your browser, and supports a wide range of graph types. In this part of the guide, we’ll go over how to use WebPlotDigitizer effectively.
To begin, visit the WebPlotDigitizer site and upload your graph image. You’ll be asked to select the chart type. After that, you’ll calibrate the axes by clicking on known values along the X and Y lines. This helps the tool align the graph’s scale with its detection system.
Once calibrated, you can choose between manual or automatic data extraction. If your graph is clean and the points are well-defined, automatic mode can scan and detect the data quickly. Just drag over the area containing the data points, and the tool will highlight what it finds. For more control, use manual mode to click on individual points.
As you mark the points, a panel on the side displays the extracted data in real-time. You can then export this data as a CSV or JSON file, depending on your needs. It’s a good idea to review the image closely before exporting, as the auto-detection might occasionally misread overlapping elements or faded lines.
Conclusion
Getting accurate data from graph images used to be a slow, manual process. However, the tools listed here make it easier to capture that data quickly and reliably. Whether you’re working on research, reviewing reports, or just need a way to turn visual information into numbers, there’s something here that fits your needs. Each tool brings a different approach, but if ease of use and precision are your main priorities, WebPlotDigitizer is a great place to start.
Related Articles
PowerPoint Image Compression: Reduce File Size Without Sacrificing Clarity
Best Image to PDF Converters for Desktop: 6 Top Picks

The Ultimate Guide to Free Copyright-Free HD Picture Sources

Top 7 Best AI Image Pixel Resizers for Perfect Image Quality

The 6 Best Free Stock Photo Sites in 2025 for Stunning Visuals Without the Price Tag

Easily Extract Key Data from Emails Using Parsio
Popular Articles

How to Detect AI-Generated Text and Photos in a World of Digital Deception

Thunderbird 136 Launches with Smarter Threading and Dark Reader

Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Captions to Instagram Reels

Remini Video Enhancer Review: Transform Your Videos with AI Technology

Top 7z File Unlocking Software for Secure Access

ActiveCampaign vs. tinyEmail: Comparing the Best Email Marketing Tools

Convert VOB Files to 3GP: Top Tools for 3G Mobile Devices

Best Free PDF to Image Tools for Quick and Easy Conversion

Magisto: The Simplified Approach to Video Editing for Quick and Effective Content

How to Repair DLL Errors on Windows 10 for Free: 5 Tools

Best MXF to MKV Converters That Actually Work

 mww2
mww2